by — VigiPay Strategy Team
Introduction
The Naira has long been central to economic debates, with many predicting continued depreciation. Recently, Nairametrics published an article suggesting that the Naira could weaken in 2025, citing speculative risks. But here’s the thing—their argument lacks strong fundamental backing.
What if we told you the Naira could actually appreciate in 2025? It may sound unlikely, but a different picture emerges when we analyze the data.
First, let’s commend the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) for introducing the Nigeria Foreign Exchange Market Electronic Trading System (NFEM EFEMS) via Bloomberg’s BMatch System—a move that has significantly improved price discovery, transparency, and liquidity in the FX market. The impact has been immediate: the Naira has appreciated from ₦1,673/$ (closing rate on December 2, 2024) to just above ₦1,500 (within a ±₦15 range) in the first two weeks of February 2025. This shows growing market confidence and improved FX management.
With this premise, let’s take a data-driven approach to examine why the Naira could strengthen in 2025.
We’ll break this report into 6 key areas:
✅ What Determines the Strength of a Currency?
✅ Nigeria’s Trade Performance: A Positive Outlook
✅ Forex Reserves and USD Supply: More Dollars, Less Pressure
✅ Fiscal & Monetary Policy: A Proactive Approach
✅ External Factors That Could Influence the Naira Positively or Negatively
✅ Recommendations: What Needs to Happen Next?
1. What Determines the Strength of a Currency?
A currency’s value is shaped by key economic fundamentals, not just market speculation. The major factors include:
- Balance of Trade – If a country exports more than it imports, it accumulates foreign exchange reserves, strengthening its currency.
- Forex Reserves – Higher reserves give central banks the power to stabilize the currency or intervene in the market.
- Inflation Control – Lower inflation preserves purchasing power and builds investor confidence.
- Foreign Exchange Inflows – Remittances, foreign direct investment (FDI), and foreign portfolio investment (FPI) increase FX supply.
- Monetary & Fiscal Policy – Government spending, interest rates, and central bank policies are crucial for currency stability.
Let’s analyze how Nigeria is performing on these fronts.
2. Nigeria’s Trade Performance: A Positive Outlook
Exports Are Growing
Nigeria’s export engine is picking up steam, and it’s no longer just about oil. While oil still dominates (about 70% of total exports), non-oil exports are quietly making gains.
- Oil Exports: Oil production has been steadily increasing:
- 2022: 1.37 million barrels per day (bpd)
- 2023: 1.43 million bpd
- 2024: 1.55 million bpd
- 2025 (Projected): 1.74 million bpd* (potentially reaching 2.1 million bpd, per NUPRC)
Source: NBS, 2024
- Non-Oil Exports: The agriculture (sesame, cocoa, cashew), solid minerals, and manufacturing sectors are expanding. According to NEPC, non-oil exports were $5.45 billion in 2024, representing 20.7% YoY growth over 2023. Reports from the WTO Policy Review show that the share of non-oil exports in total exports doubled between 2017 and 2023, consisting primarily of agricultural products, fertilizer, and metals. Below is a table showing the values and volumes of non-oil exports in Nigeria between 2021 and 2024:
Non Oil Exports (2021-2024)
| Year | Value (in $’bn) | Volume (in million metric tonnes) |
| 2021 | 3.44 | – |
| 2022 | 4.82 | 4.41 |
| 2023 | 4.52 | 6.70 |
| 2024 | 5.45 | 7.20 |
Source: NEPC, 2024
- The Dangote Refinery Effect: The refinery has already started reducing fuel imports and has even exported PMS to Ghana, Cameroon, Angola, and South Africa. Recently, Dangote Group announced sales of two jet fuel cargoes to Saudi Aramco, adding a new FX inflow stream.
It’s worth noting that the BUA 200,000 bpd Refinery is in the works and could launch in 2025 according to reports.
*As of January 2025
Imports Are Declining
One of the biggest drains on FX reserves has been refined petroleum imports. But with the Dangote Refinery ramping up, Nigeria will significantly cut down on fuel imports, reducing demand for the dollar. The refinery can supply 100% of Nigeria’s domestic fuel needs at full capacity (650,000bpd), with enough surplus for export.
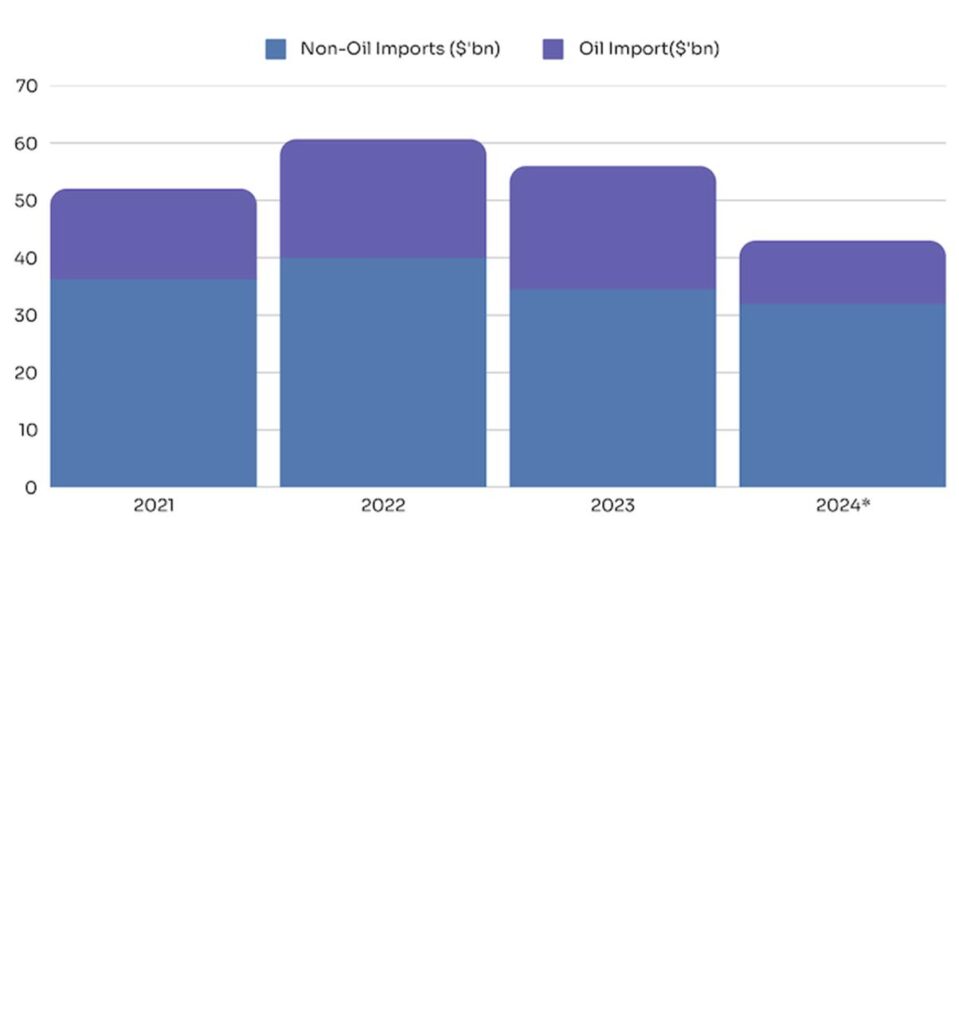
*2024 data is projected considering the trends in the first-three quarters and the realities of petroleum imports in H2 2024.
Source: WITS, 2024
Therefore, net imports could reduce significantly in 2025 as Nigeria sources its petroleum products locally.
Balance of Trade Surplus
According to NBS data, Nigeria recorded a ₦19.3 trillion trade surplus in the first three quarters of 2024—a massive leap from:
- ₦44.77 billion in 2023
- ₦1.2 trillion in 2022
- -₦1.94 trillion in 2021
The trade surplus in just the first three quarters of 2024 is 15x and 429.6x larger than the full-year surpluses of 2022 and 2023, respectively.
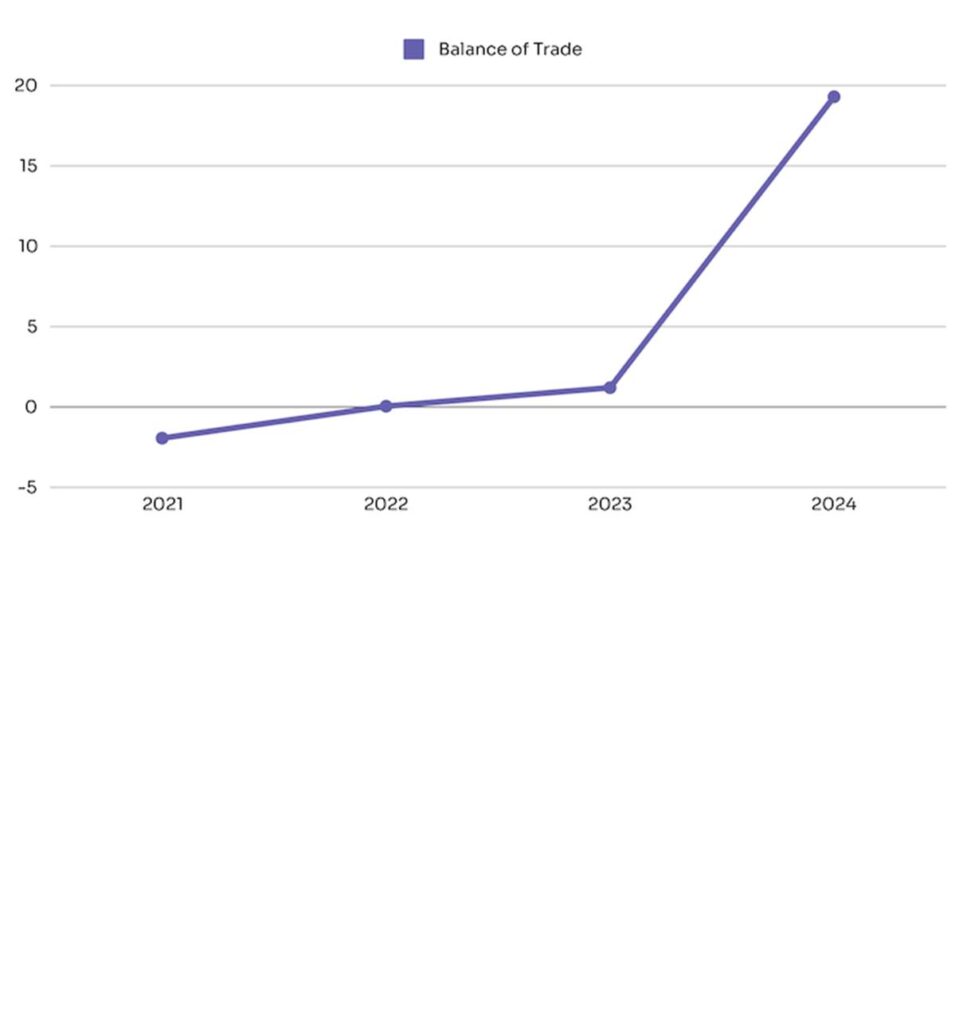
Source: NBS, 2024
Why This Matters
A positive trade balance means more FX supply than demand—a crucial factor for currency appreciation.
3. Forex Reserves and USD Supply: More Dollars, Less Pressure
Nigeria’s FX position is improving:
- CBN’s Forex Reserves Are Rebounding – As of December 2024, FX reserves stood at $40.9 billion, marking a 24% increase from 2023 and 10% from 2022. This gives the CBN more room to manage liquidity.
- IMTO & Remittance Inflows Are Rising – Remittances remain a strong FX source. According to the CBN, remittance inflows grew by 61% YoY in the first nine months of 2024—from $2.62 billion to $4.22 billion. This growth is expected to continue due to:
- A more structured FX market
- Better CBN-IMTO relationships
- Increased overall economic confidence
- Foreign Investments Are Returning – With market reforms, FDI and FPI inflows are increasing, adding FX liquidity. According to NBS, Nigeria received $7.3 billion in foreign investment inflows in the first three quarters of 2024, reflecting:
- 87% growth over 2023
- 38% over 2022
- 9% over 2021
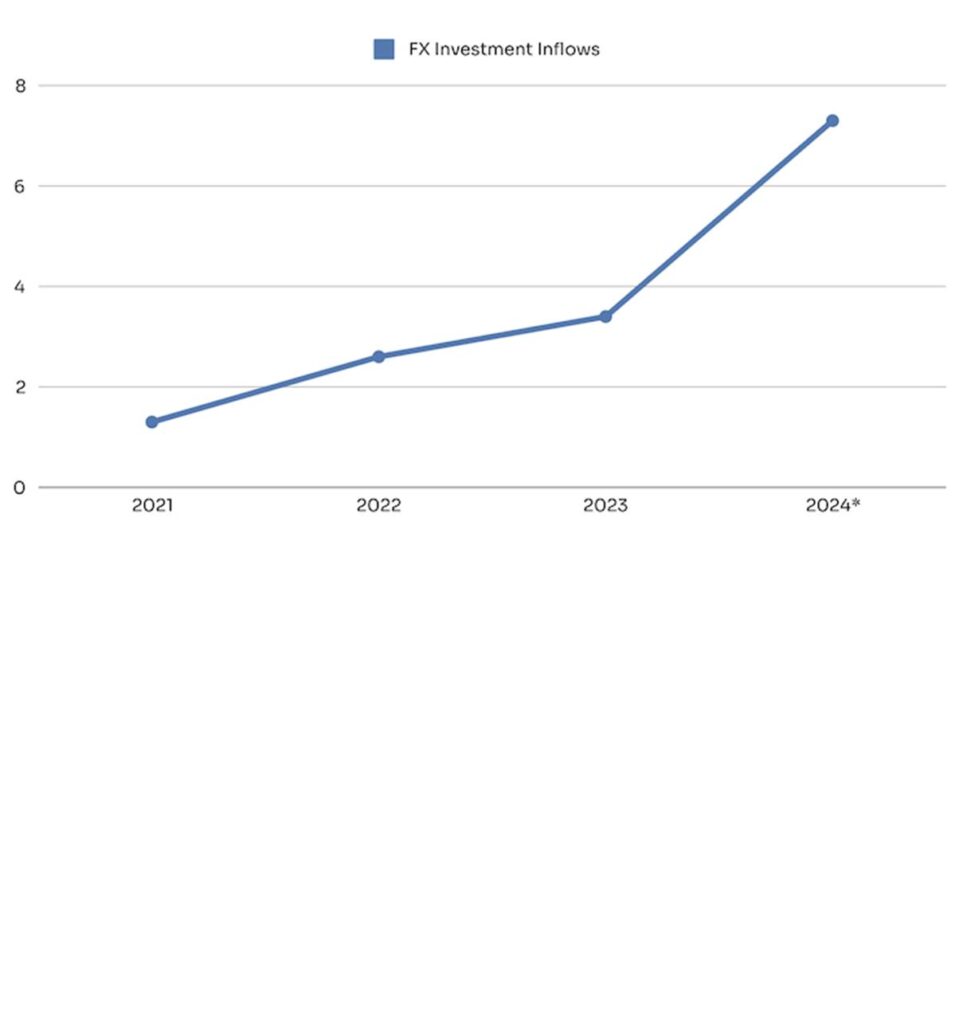
Source: Trade Economics, 2024
Impact on the Naira
Higher reserves allow the CBN to defend the Naira against volatility, boosting investor confidence.
4. Fiscal & Monetary Policy: A Proactive Approach
Nigeria’s 2025 Budget: A Currency-Friendly Strategy
The 2025 “Budget of Restoration” focuses on strengthening economic fundamentals through:
- Reduced reliance on external borrowing – Lower FX exposure and demand for dollars to service debt.
- Higher revenue targets – Expanding non-oil income sources to shield Nigeria from oil price volatility.
- Increased capital investment – Infrastructure spending to boost local production and reduce import dependency.
CBN’s Policy Direction
- Higher interest rates attract foreign capital – Nigeria’s tight monetary policy is boosting investor confidence.
- Inflation is stabilizing – The Federal Government targets 15% inflation in 2025, supported by improved macroeconomic indicators:
- PMS prices have improved – Dangote’s ex-depot price has reduced to ₦890/litre from ₦950 in February 2025.
- Food prices are declining, easing inflationary pressures.
- FX market reforms improve transparency – A more structured FX market reduces speculation-driven volatility.
Why This Matters
These factors combined to position the Naira for a stronger 2025 rather than a decline.
5. External Factors That Could Influence the Naira Positively or Negatively
Beyond domestic fundamentals, global events also play a role in shaping the Naira’s trajectory. While some of these factors pose risks, others could favour a stronger Naira in 2025.
- Geo-political Tensions & Oil Prices – Conflicts in the Middle East, the Russia-Ukraine war, and OPEC+ production decisions could increase oil prices. Since crude oil is Nigeria’s primary FX earner, high prices would increase FX inflow and strengthen the Naira.
- Trumponomics & U.S. Monetary Policy – With Donald Trump back in the White House, his economic policies could reshape global markets. A weaker U.S. dollar from potential trade wars or softer Fed policies could make emerging market currencies (including the Naira) more attractive. However, if Trump pushes for aggressive rate hikes, FX outflows from Nigeria could increase—but Nigeria’s improving fundamentals could mitigate this.
- China’s Economic Slowdown – While a weaker Chinese economy may reduce global demand for commodities, it could lower the cost of imports for Nigeria, reducing FX demand. Additionally, if China redirects investments to Africa, Nigeria could benefit from increased FDI and infrastructure funding.
- Global Shift to Alternative Energy – The gradual transition to renewable energy is reshaping global oil demand, but in the short term, Nigeria could benefit from increased investment in gas exports, particularly as Europe looks for alternatives to Russian energy.
- Regional Trade Agreements – Deeper integration within the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) could drive higher non-oil exports, creating additional FX inflows and reducing reliance on dollar-heavy trade routes.
6. Recommendations: What Needs to Happen Next?
For the Naira to strengthen in 2025, the government, private sector, and citizens must be intentional. Here’s what needs to be done
For the Government:
✅ Expand export incentives to boost non-oil revenue by increasing financial support for exporters, reducing bureaucratic bottlenecks, and implementing a clear, predictable export tax rebate scheme.
✅ Strengthen local production to reduce import dependency by providing targeted subsidies to manufacturers sourcing raw materials locally, enforcing policies fostering backward integration, and reducing tariffs on essential production inputs.
✅ Improve infrastructure to attract higher foreign investment by prioritizing energy sector reforms, improving road and port logistics to ease trade, and implementing stable investment-friendly policies that encourage long-term capital inflows.
✅ The CBN must intensify its efforts to maintain a stable FX market by implementing a predictable FX framework to curb speculation and ensure confidence in the market. Clear communication on policy direction will also help manage expectations and reduce market volatility.
✅ Accelerate FX repatriation policies by ensuring swift settlement of exporters’ proceeds, strengthening relationships with IMTOs to improve remittance inflows, and enforcing compliance among multinational firms repatriating profits.
For the Private Sector & Traders:
✅Leverage government incentives to scale exports by tapping into NEPC grants, participating in the AfCFTA framework, and identifying high-growth regional markets for Nigerian products.
✅ Reduce reliance on imported raw materials by sourcing alternative local materials, investing in R&D for product substitution, and partnering with local suppliers to build resilient supply chains.
✅Innovate around local manufacturing and industrialisation by adopting cost-efficient production methods, collaborating on shared industrial clusters, and securing government-backed financing to expand production capacity.
For Nigerian Citizens:
✅ Buy Nigeria – Support locally made products to reduce FX pressure by prioritizing Nigerian brands for everyday purchases, creating demand for homegrown industries, and encouraging businesses to scale.
✅ Invest in assets that hedge against inflation and currency risks by diversifying into stable investments such as government bonds, real estate, and export-driven businesses rather than holding excess foreign currency.
✅ Advocate for pro-business and pro-export government policies by engaging policymakers, supporting initiatives promoting local production, and staying informed on macroeconomic policies affecting currency stability.
Conclusion: The Case for a Stronger Naira
The idea that the Naira will weaken in 2025 isn’t backed by solid fundamentals. Instead, the data suggests:
✅ A strong trade surplus – Exports are rising while imports decline.
✅ Improved forex reserves – More dollar liquidity to stabilize the currency.
✅ Proactive fiscal & monetary policies – Supporting economic stability.
Of course, challenges remain, but the foundation for a currency rebound is stronger than many assume. Instead of bracing for a decline, Nigeria should prepare for a potential appreciation—and take the right steps to make it happen.


